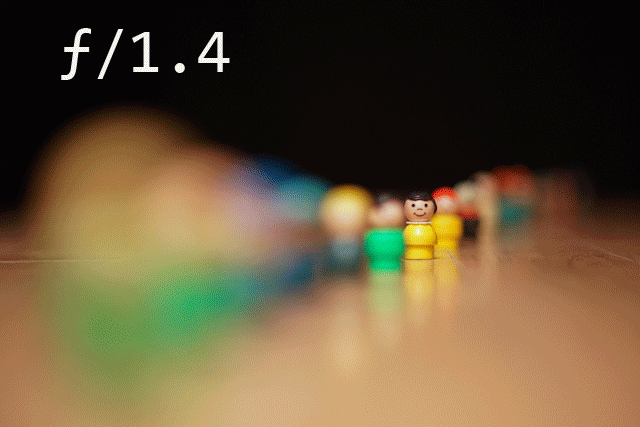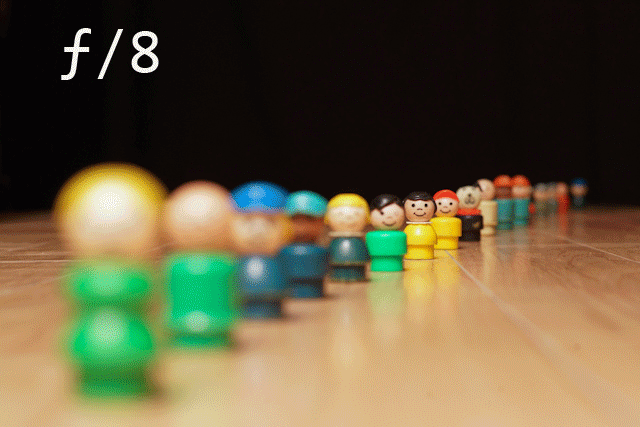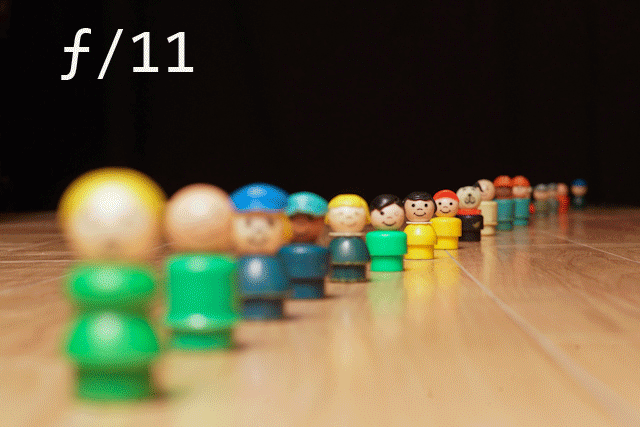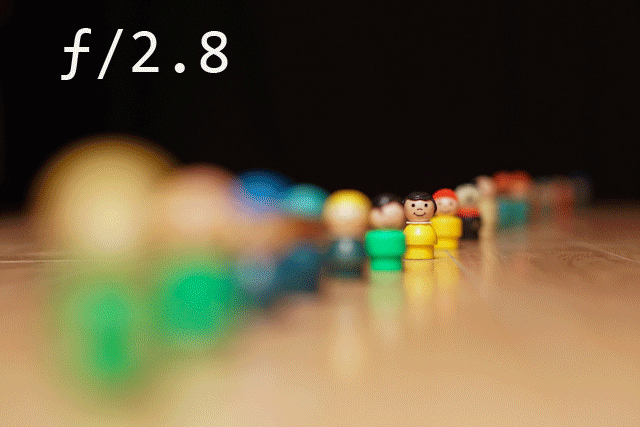On my previous blog posts, I have listed a number of directorial inspirations who all shape my creative endeavour in the industry. I focused on Studio Ghibli’s master filmmaker Hayao Miayazaki for a number of reasons that are all encompassed under simplicity and the essence of the human condition. I would like to point out one of the main reasons as to why I think the 2D animation of Studio Ghibli (complemented superbly by a powerful and evoking story), encapsulates this simplicity and essence in an almost indecipherable way to those who are entranced by them:
Static Movement.
You may think that this is a contradiction, but I’ll give you a few scrolls down to see for yourself the very meaning of this phrase.




I inundated myself with titles upon titles from Studio Ghibli and of the same type of animated feature films as an investigative initiative, propelling myself to come down to a conclusion as to why animated feature films really does “soothe the spirit” and envelop you in its fictional reality better than some fictional realities of non-animated feature films.
I found Julien Douvier‘s cinemagraphs, a combination of cinema and photography (black and white photos above), as the answer to the enigma of static movement. Miyazaki doesn’t just choose a certain character (mostly the protagonist) in his films to show movement and action, but he complements this with one another feature in the scene that moves before he completely makes everything else static so the viewers are attuned to only what moves. Miyazaki builds upon the innate ability of humans to sense movement and draws his viewers through this and the explicitness of it, thus making for a profound play on the senses.
Example: the everyday and the mundane

Miyazaki juxtaposes the idiosyncrasies of fantasy and realism in an understated energy that flows though the powerful tool of scene selections. The sounds of the scratching of pen on paper, the scene of the protagonist turning a prawn tempura cooking on oil (above), or even a character simply breathing. In previous studies of films and even in writing books and novels, most discourage the inclusion of the everyday, the mundane or the innate (the human elements that we take for granted i.e. breathing) for it does not egg the story on.
But that is the power behind these films: the marriage of static movement and the inclusion of the mundane. Instead of jarring the viewers, they are instead given a different form of entry into the world of the characters that you are following on screen, you are given entry to not just what matters to the advancement of the story, but to them as characters whether they be a child or an adult, a slippery monster or a gigantic frog.
Technicalities:
I did my internship with a great team, super talented, incredibly professional and who knew the ins and outs the film life very well. I admired the director because she knew exactly what kind of shot she wanted and what lens to use specifically in each shot and when the cinematographer would ask if this length is good, she would sometimes agree and sometimes she would suggest a different length instead and I know for sure that to learn this is very very supercalifragilisticexpialidocious- important.
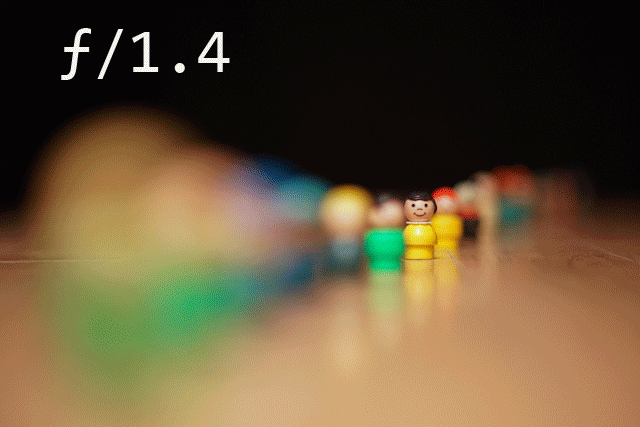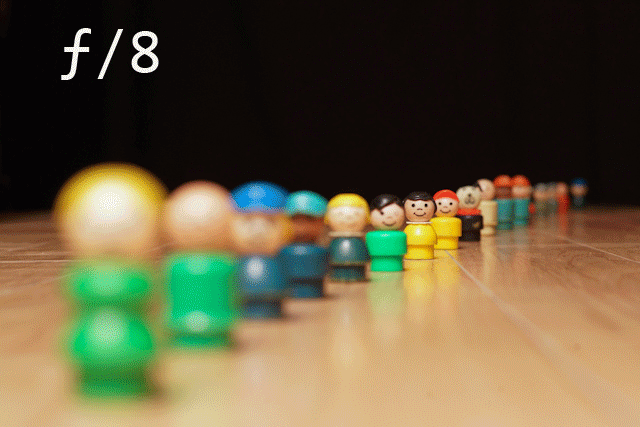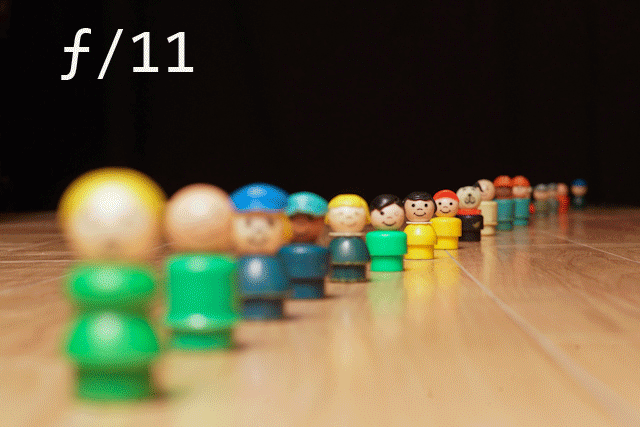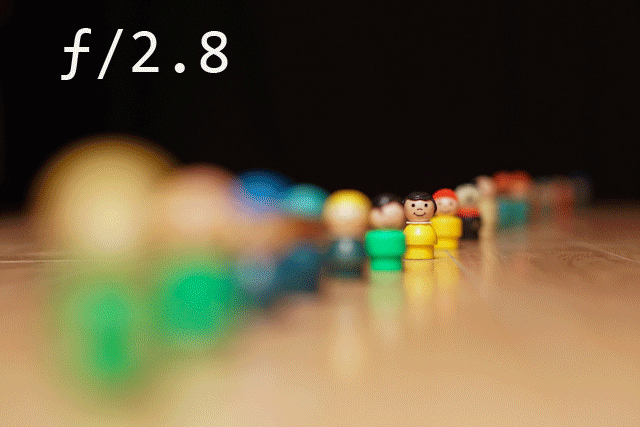

These above gifs make it seem really simple and easy but how does one actually do it? Please, someone actually explain this to me because I will be extremely grateful. And depth of field, I am still very much at a loss as to how to calculate this and how to actually do this using a cameras but I WILL KNOW by the end of this class and don’t you forget it!
Anywho,
Inspired:
Under this context, I venture off in this class particularly, to study the elements of cinemagraph (how exactly to do this using a video camera) and static movement, and to play around with characters and actions and cinematography that would yield results similar to above: an experience of the human condition and the simplicity of realism and fantasy at the same time.
I am also very much interested in learning the the basic technicalities of types of lenses and depth of field to be able to further experiment and successfully make happen combination of cinemagraph and static movement for my final project.
Final Project Inspiration:
For my final project, I have decided to research, build upon and produce a project that is focused on static movement. This could be a non-animated short that feels like and is shot using the principles of static movement and cinemagraph. More on this very soon!